In recent years, the resurgence of interest in cultural heritage and historical architecture has sparked a series of government-led restoration initiatives around the globe. These policies have played a pivotal role in the preservation and revitalization of iconic structures, breathing new life into landmarks that bear witness to our shared past. Understanding the multifaceted approaches to these restoration projects offers insight into how nations are preserving their historical identity while also driving economic and cultural revitalization.
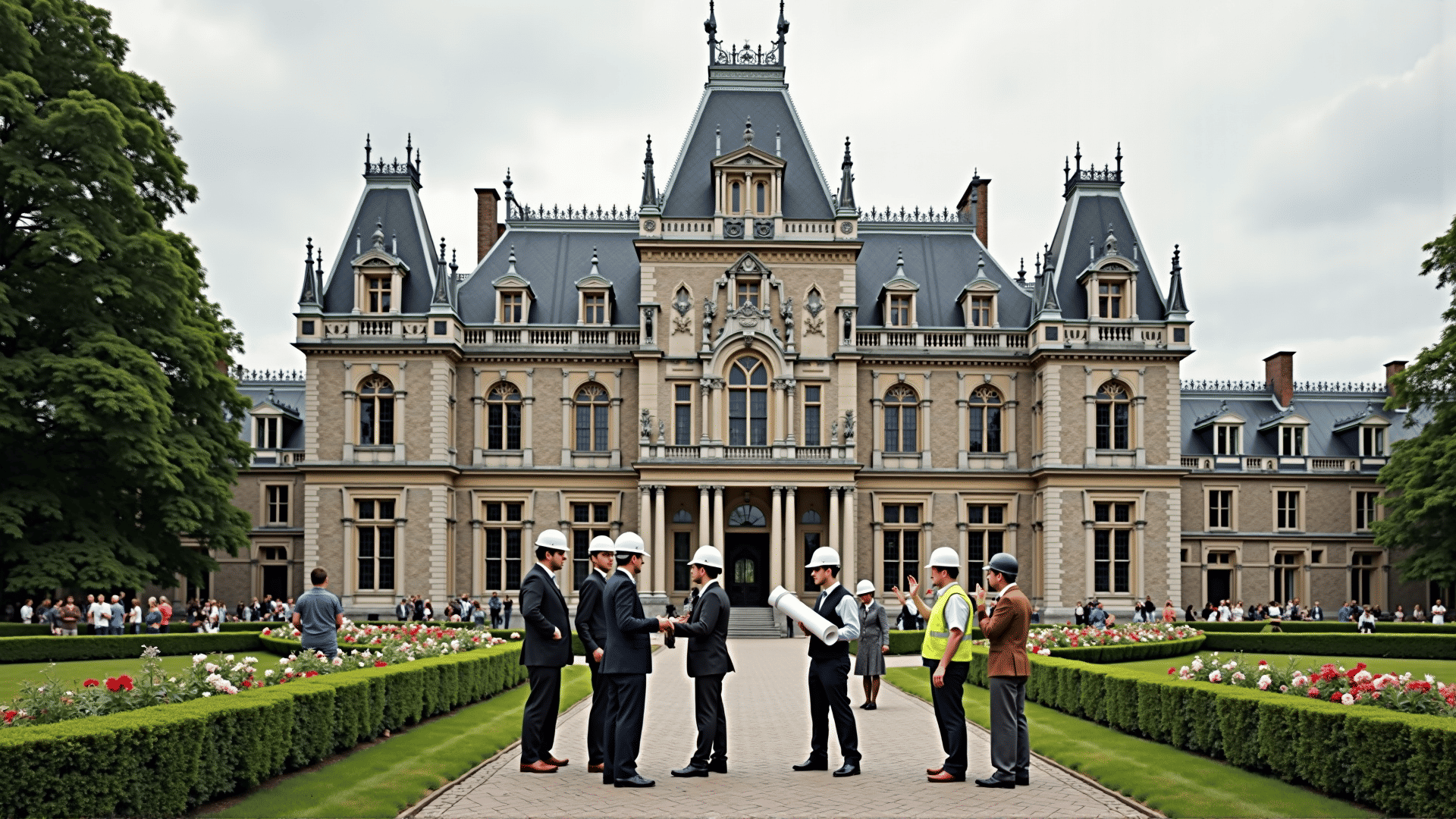
One of the central tenets of these restoration policies is the recognition of cultural heritage as a vital asset. Many governments have come to realize that iconic structures are not just relics of the past but are integral to a country's identity and continuity. This acknowledgment has led to increased funding and legislative measures aimed at safeguarding these structures, often enlisting the expertise of historians, architects, and conservators to lead restoration efforts.
A crucial strategy has been the integration of modern technology with traditional restoration techniques. The use of digital scanning and modeling technology allows restoration teams to meticulously analyze the structural and aesthetic elements of a building, often uncovering details that have been lost over time. This technology ensures precision in restoration, enabling teams to recreate historical features with a high degree of accuracy.
Furthermore, many governments are adopting participatory approaches, involving local communities in the restoration process. This inclusion fosters a sense of ownership and pride, as communities are directly engaged in preserving their heritage. Local involvement often encompasses not only the physical restoration but also the promotion of traditional crafts and skills, which are essential for maintaining the authenticity of historical structures.
In addition to preserving cultural heritage, these restoration projects have significant economic implications. Restored landmarks often become tourist attractions, stimulating local economies and providing jobs. The rise of cultural tourism has prompted governments to invest in infrastructure surrounding these sites, improving accessibility and amenities. This, in turn, has a ripple effect, revitalizing urban areas and supporting local businesses.
Education also plays a central role in government-led restoration policies. Many initiatives include educational programs aimed at raising public awareness about the importance of preserving historical structures. These programs often involve schools, universities, and cultural organizations, providing opportunities for students and professionals to engage with history hands-on. Education not only ensures the transmission of traditional knowledge but also inspires future generations to continue preservation efforts.
Challenges do exist, however, particularly in balancing modern use with historical preservation. Many historic buildings face the dilemma of needing to accommodate contemporary functionalities while maintaining their architectural integrity. Governments often address this by implementing adaptive reuse policies, which repurpose historic structures for modern-day use without altering their essential characteristics.
Ultimately, government-led restoration initiatives exemplify a commitment to the values of heritage and a dedication to safeguarding these legacies for future generations. These efforts ensure that iconic structures stand not only as monuments to the past but also as vibrant components of present-day cultural and communal life. By embracing innovative techniques, fostering community involvement, and prioritizing education, governments worldwide are crafting a harmonious blend between the preservation of heritage and the pursuit of progress.